This post may contain affiliate links.
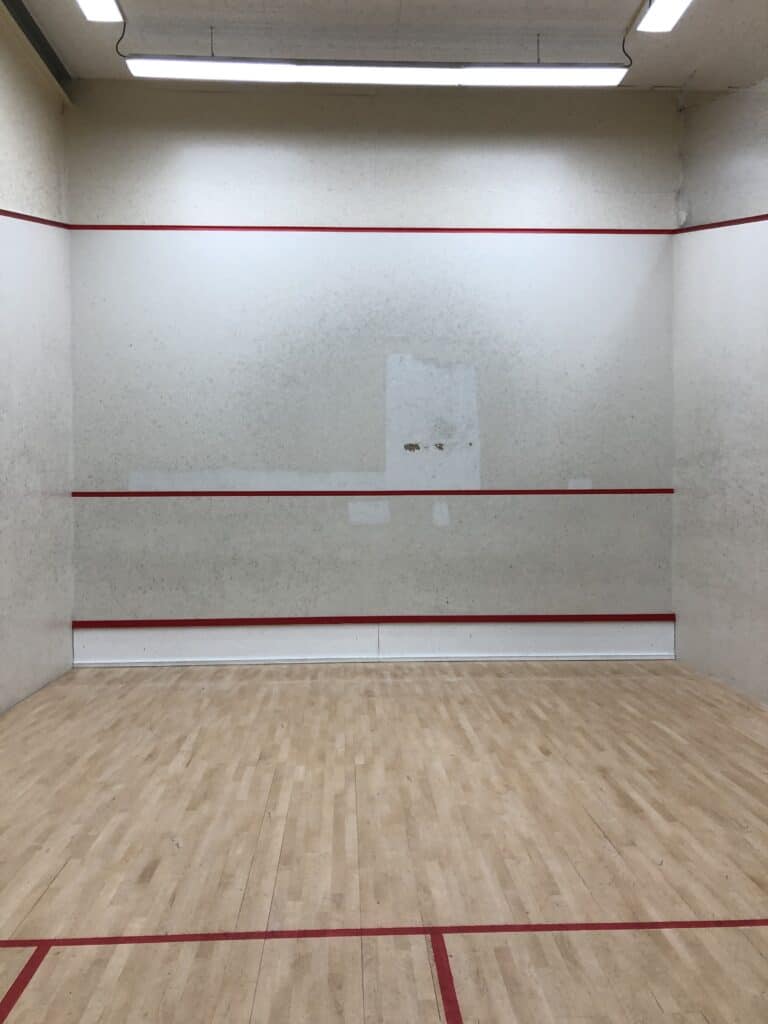

Having played on different squash courts, both older and newer ones, I can attest they feel different. Since I was not yet able to exactly pinpoint the cause, I took the structured approach. Therefore I looked first at what squash courts are actually made of.
Wood (hardwood, plywood), glass, steel, drywall, foam, rubber, metal, and concrete are the most prevalent materials used for squash courts. Glass tends to be used more often for newer and more professional court walls, whereas panels and drywall are often used for older courts.
Having noted down the different materials may seem sufficient at a first glance. However, looking at it in more detail is worthwhile, since several materials are used for multiple parts of the court.
What are the parts of a squash court?
A squash court consists of a floor and four surrounding walls, being a front wall, two side walls, and the back wall. Since not all walls use the same materials, let us look at the most common constructions for each of the walls.
Overview
| Part of the court | Used materials |
| Front wall | • Front wall panels • Steel or wooden frame • Foam (fire-resistant soundproofing) • Drywall or plywood • Metal (tin) |
| Side walls | • Side wall panels • Steel or wooden frame • Foam (fire-resistant soundproofing) • Drywall or plywood • Nylon (net between courts) |
| Back wall | • Tempered glass (panels and door) |
| Floor | • Hardwood solid floor or engineered floor • Plywood • Wooden sleepers • Rubber • Concrete |
| Miscellaneous | • Lights • Line marking paint • Seats of varying materials • Camera and video considerations • Heating and ventilation systems |
Front wall
The front wall is typically made up of steel frames, while a wooden frame is also possible. The frame is filled with fire-resistant soundproofing. This construction is typically covered with drywall, but it is also common to use plywood. Although allowed, front walls are rarely made out of glass.
Next to that, it is common practice to put front wall panels only on the playing part of the front wall. These front wall panels are certified by the World Squash Federation (WSF), see accredited suppliers. The rest of the front wall is only covered with drywall or plywood.
The playing part on the front wall is marked as the area between two red line-markings, namely from the (top) front wall line to the tin below. However, during the service, the playing part on the front wall is smaller. Then it consists of only the area between the (top) front wall line and the service line.
it is common practice is to put front wall panels only on the playing part of the front wall.
Tin
The tin is generally made of metal and is rounded in its shape in order to deflect the ball while hitting. Although metal is not a hard requirement for the tin, it needs to give a distinctive sound when the ball hits the tin. Electronic devices that generate sounds when the ball makes contact are therefore also a viable option. To make it stand out visibly the tin is painted in the same (red) color as the other line markings.
The tin is located 45 cm above the floor and added onto the front wall panels. To make it stand out additional front panels are added below the tin, also called the tin board. It is also allowed and common to put any logo or name from either the club or sponsors below on the tin board (or above the playing part of the front wall).
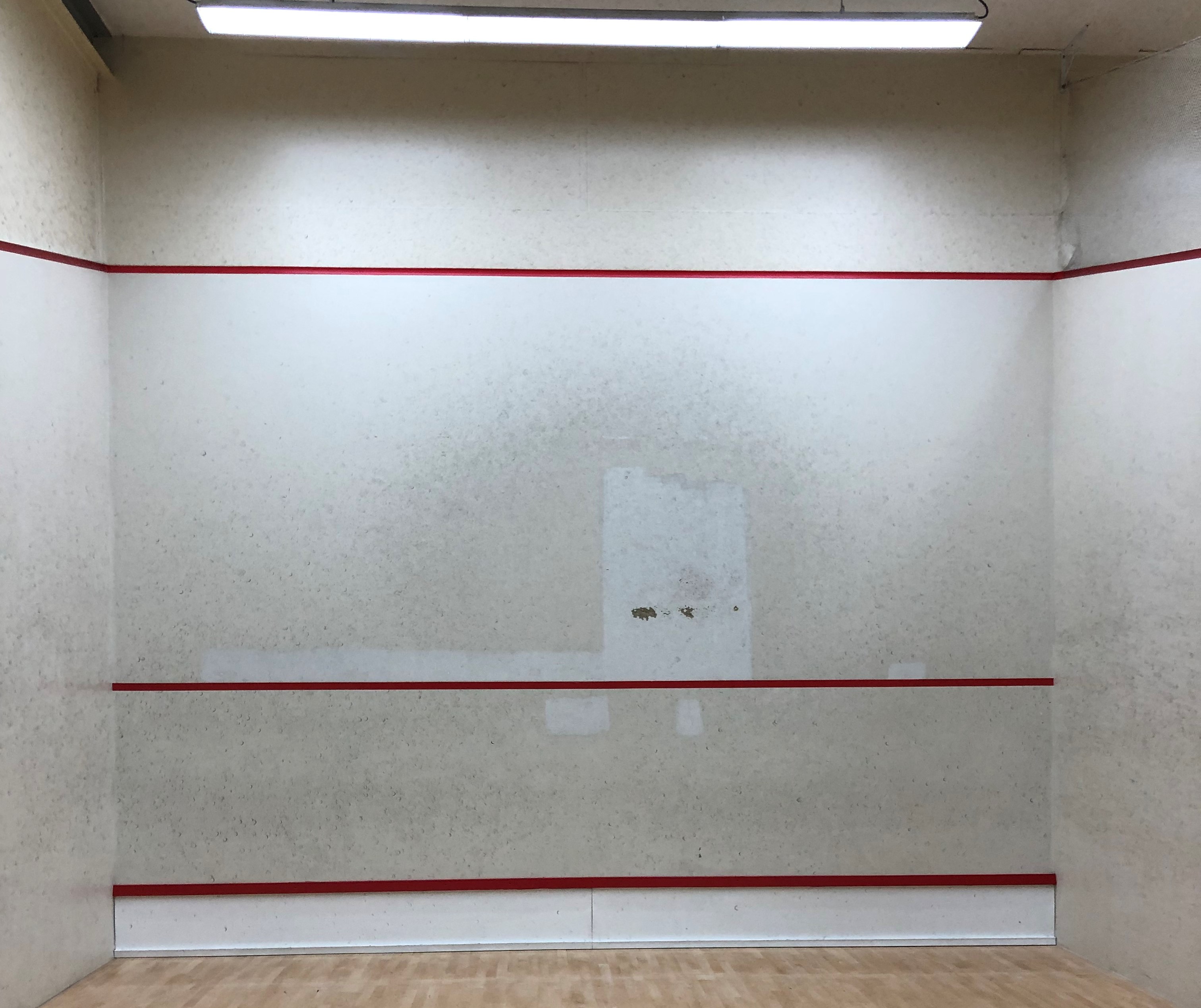

Side walls
The side walls are most commonly made out of the same construction as the front wall. This means, a steel or wooden frame filled with fire-resistant fireproofing and covered with drywall or plywood. Just like the front wall panels, it is common practice is to put panels only on the playing part of the sidewall. The non-playing part of the side walls is extended with drywall or contains a nylon net to separate the courts.
However, glass is also used, especially for professional courts to allow a larger audience to attend the matches. It also supports the streaming and broadcasting of the matches. This glass is specially designed for these squash courts and therefore certified by the WSF, see accredited suppliers.
The playing part on the side walls is marked as the area below the red line marking.
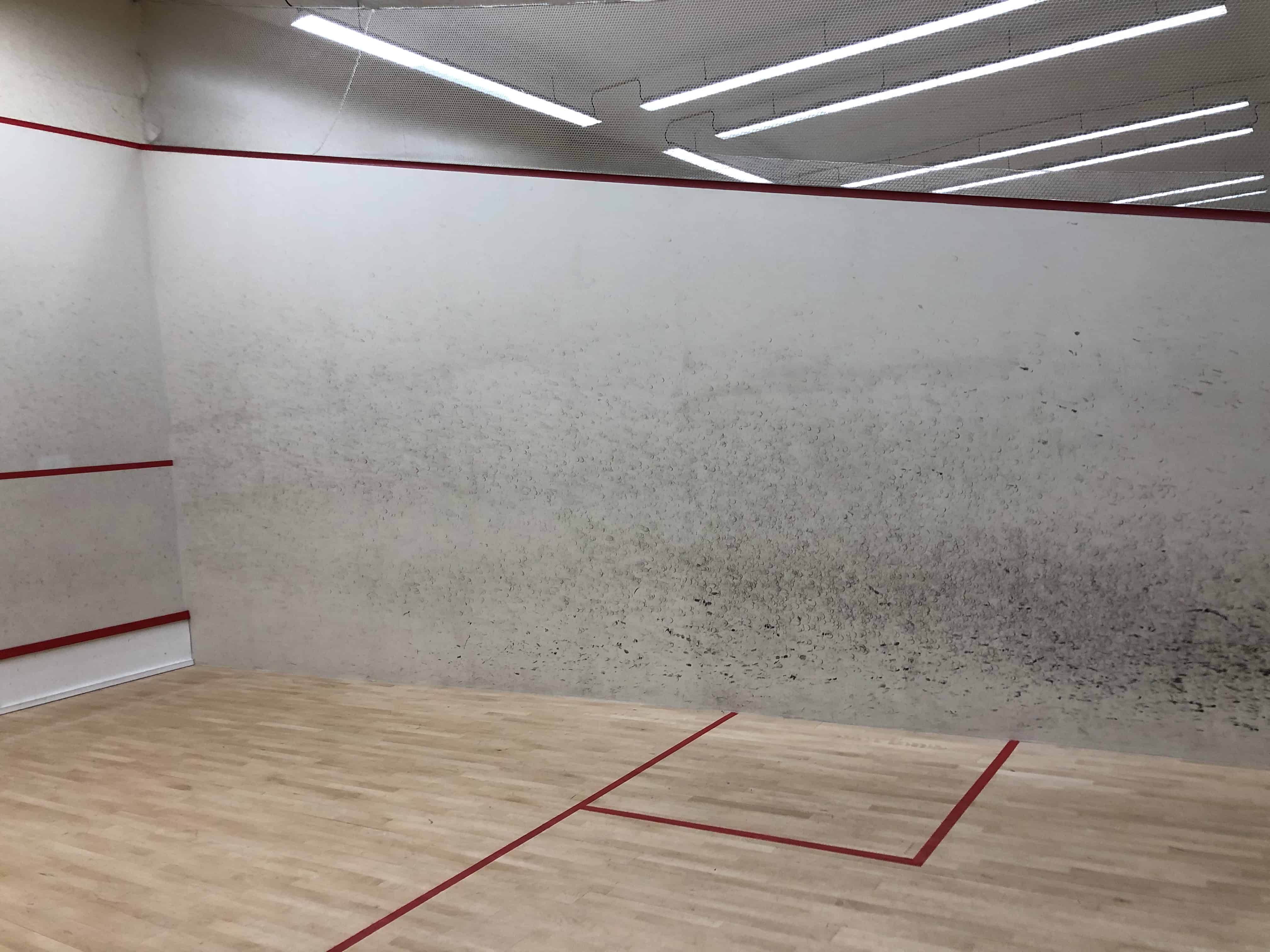

Back wall
The back wall is generally made of tempered (safety) glass, consisting of two glass panels and one glass door. All glass windows, including the door, are supported by glass panels horizontally placed on the outside of the court. Just like the side walls, specifically designed glass is used that is certified by the WSF, see accredited suppliers.
The door opens into the courts to avoid any player falling through the door while bumping into it. In order to open from the inside, the door contains a hole. This prevents either the ball or players to hit any protrusive objects.
However, you may encounter old courts without any glass and a balcony view of the court itself. The usage of glass has been increased to accommodate the increasing audience.
The playing part on the back wall is marked as the area below the red line marking.

Flooring
The floor of a squash court is either classified as solid or engineered. Solid floors are made of unsealed hardwood (typically maple or beech) and contain a matt uncolored finish. These solid floors are often used in leisure centers according to one of the court floor manufacturers . Engineered board floors, on the other hand, are made of plywood with hardwood on top. These unsealed boards also contain a matt uncolored finish, but cannot be sanded as much as solid floors. Therefore these engineered boards are used in traditional squash clubs. It is worth noting that many manufacturers of both types of flooring are certified by the World Squash Federation (WSF), see accredited suppliers.
. Engineered board floors, on the other hand, are made of plywood with hardwood on top. These unsealed boards also contain a matt uncolored finish, but cannot be sanded as much as solid floors. Therefore these engineered boards are used in traditional squash clubs. It is worth noting that many manufacturers of both types of flooring are certified by the World Squash Federation (WSF), see accredited suppliers.
Below the wooden floor lies a leveled subfloor (plywood on top of sleepers). Rubber can also be used to make the subfloor more soundproof. There are multiple techniques to level the floor on uneven surfaces (mainly concrete). Another up-and-coming solution is underfloor heating. The underfloor is heated using either hot water pipes or electricity.
On top of the wooden floor, there are several red painted lines. These lines divide the court into multiple sections.
A good squash floor possesses the following qualities :
- it provides a stable surface to easily manoevre
- it is able to withstand different humidity conditions without a quick decay
- it limits the risk of players slipping and getting injured
- it is durable and lasts for years
- it can withstand relative high amounts of pressure
Miscellaneous
Lighting
In order to avoid any direct sun reflection on the court, there should be no windows above the court. Instead, artificial lighting is needed to properly and evenly illuminate the court. According to the recommendation of the WSF , for a singles court there is a minimum of 6 LED fittings and for a doubles court a minimum of 8 LED fittings.
, for a singles court there is a minimum of 6 LED fittings and for a doubles court a minimum of 8 LED fittings.
Line marking
The line marking is applied using specifically designed paint. The red-colored paint is a thick coating that will clearly mark the lines of the court.
Seating
During matches and tournaments, both the referee and the marker need to be able to see and hear the ongoing game. According to WSF regulations, squash courts need to have a dedicated space in the center behind the line of the back wall. In addition to that, video refereeing is becoming increasingly important. These officials don’t need to sit next to the courts since they need to look at the video screens. However, there still needs to be a dedicated space for them. Next to that, there will be an area for the audience to watch the match. The shape and size of this area are heavily dependent on the construction of the court.
squash courts need to have a dedicated space in the center behind the line of the back wall. In addition to that, video refereeing is becoming increasingly important. These officials don’t need to sit next to the courts since they need to look at the video screens. However, there still needs to be a dedicated space for them. Next to that, there will be an area for the audience to watch the match. The shape and size of this area are heavily dependent on the construction of the court.
Camera and video
Due to the increasing interest in the sport, matches will be broadcasted all over the world. These squash courts need to allow for the filming of the match from multiple angles. Cameras need to be placed in the walls of the courts as well as placed behind or above the court. These cameras are also accessible to the video assistant referees (VARs) to aid the referee.
Heating and ventilation
In order to allow players to perform at their best, the squash court needs to have the proper temperature and the flow of fresh air. Both air conditioning and a heating system will regulate the temperature on the court, as well as for the audience. Next to that, it needs to prevent condensation to occur, otherwise, it will quickly decay the construction of the court.
Accredited squash court suppliers
There are multiple products from several suppliers that are certified by the World Squash Federation (WSF). Many manufacturers have created their own licensed squash court solutions. This includes but is not limited to floors, walls, and lights. This link contains a list of accredited products provided by these squash court manufacturers.
contains a list of accredited products provided by these squash court manufacturers.
Recent Posts
Padel is booming in many countries around the world, but can it actually be played in all types of weather? That is why I decided to find out the impact of the weather conditions on the court and the...
In order to not present you with the secrets alone, but provide you with some context I have weaved in these secrets when discussing the following topics: How do you take care of your padel...

